Build a Schema
Utilizing the Schema Editor
JSON or XML data structures.Building a Schema
Add Properties
Click on the + (Add a child node) sign next to the root object to introduce new properties.
Name Your Property
Enter the name (or key) for the property.
Select Property Type
Choose common data types or select references to predefined schemas.
Advanced Settings
Utilize the Type Editor to assign data types, such as default values and formats, for each property.
Manage Properties
Rearrange properties by moving, copying, or deleting them. You can also embellish properties with descriptions and mark them as required.
Alternative Methods
Property Type
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| null | Represents a JSON "null" value. |
| boolean | Represents a "true" or "false" value, corresponding to the JSON "true" or "false" value. |
| object | Represents an unordered collection of key-value pairs, corresponding to the JSON "object" value. |
| array | Represents an ordered list of values, corresponding to the JSON "array" value. |
| number | Represents an arbitrary-precision, base-10 decimal number value, corresponding to the JSON "number" value. |
| string | Represents a string of Unicode characters, corresponding to the JSON "string" value. |
Array Data Type
array data type, a sub-level ITEMS property will be automatically generated. It specifies the data type of the elements within the array.Referencing Other Schemas
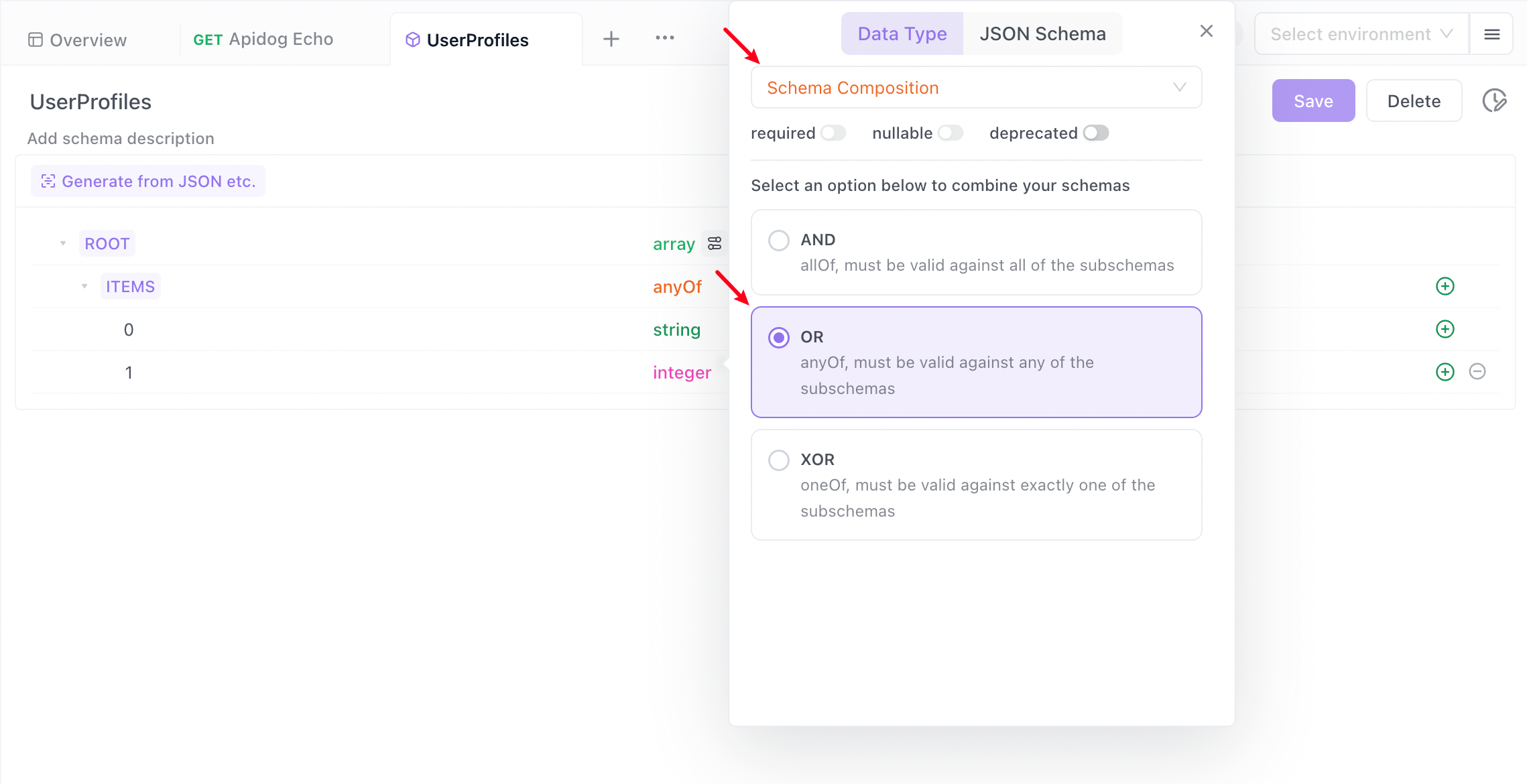
Schema Composition
| Keyword | Description |
|---|---|
| allOf (AND) | Specifies that the property must adhere to all the schemas defined in the composition. |
| anyOf (OR) | Specifies that the property can conform to any of the schemas listed in the composition. |
| oneOf (XOR) | Specifies that the property must adhere to one and only one of the schemas defined in the composition. |
Customization
Property Settings
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
| * | Indicates if the property is required. |
| N | Specifies if the property allows for null values. |
| Settings | Allows you to edit advanced settings in the Type Editor. |
Type Editor
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Enumerated Property
String, Integer, and Number types, Apidog supports enum. By toggling the enum switch, you can add enum values and descriptions. Additionally, you can perform Bulk Edit for enum values.Mock
XML Settings
HashMap, Dictionary, Array
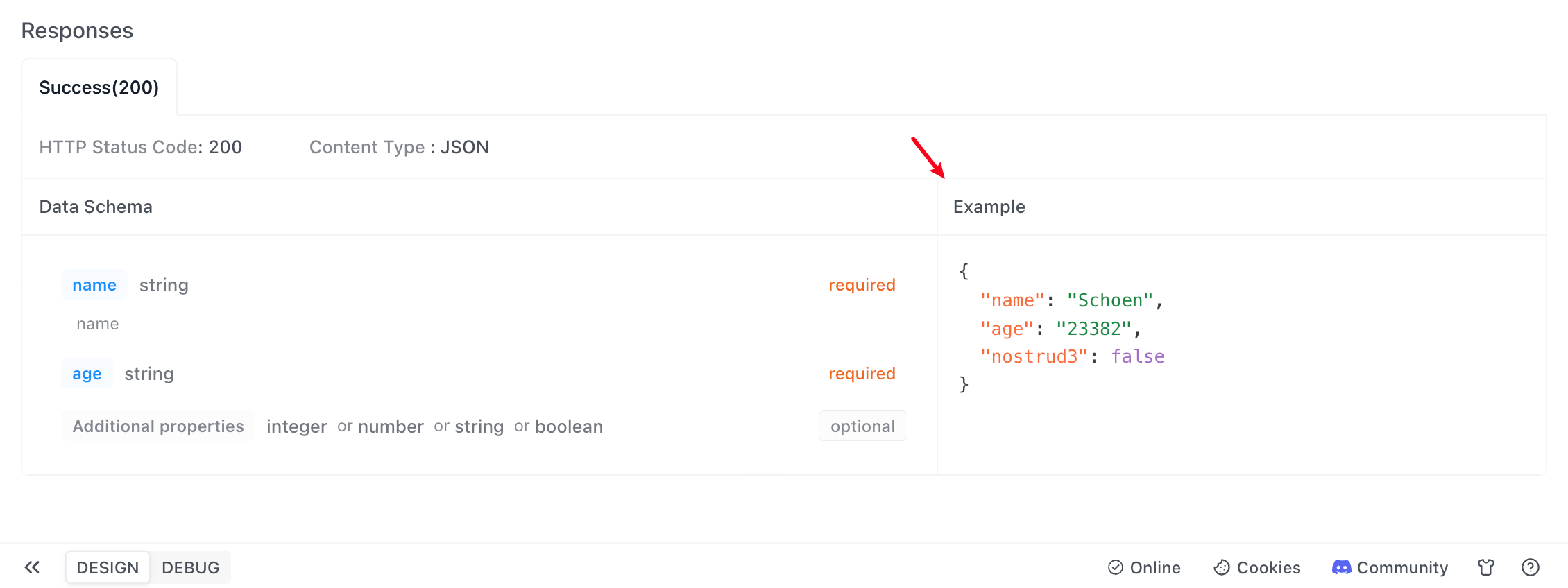
object, and then using the additionalProperties keyword to specify the type of the values in the key-value pairs.1.
2.
3.
Create a new schema and name it "UserProfiles".
In the "UserProfiles", specify the root node as an "object" type. Then click Advanced Configuration, set additionalProperties to Allow, and click the Settings button on the right.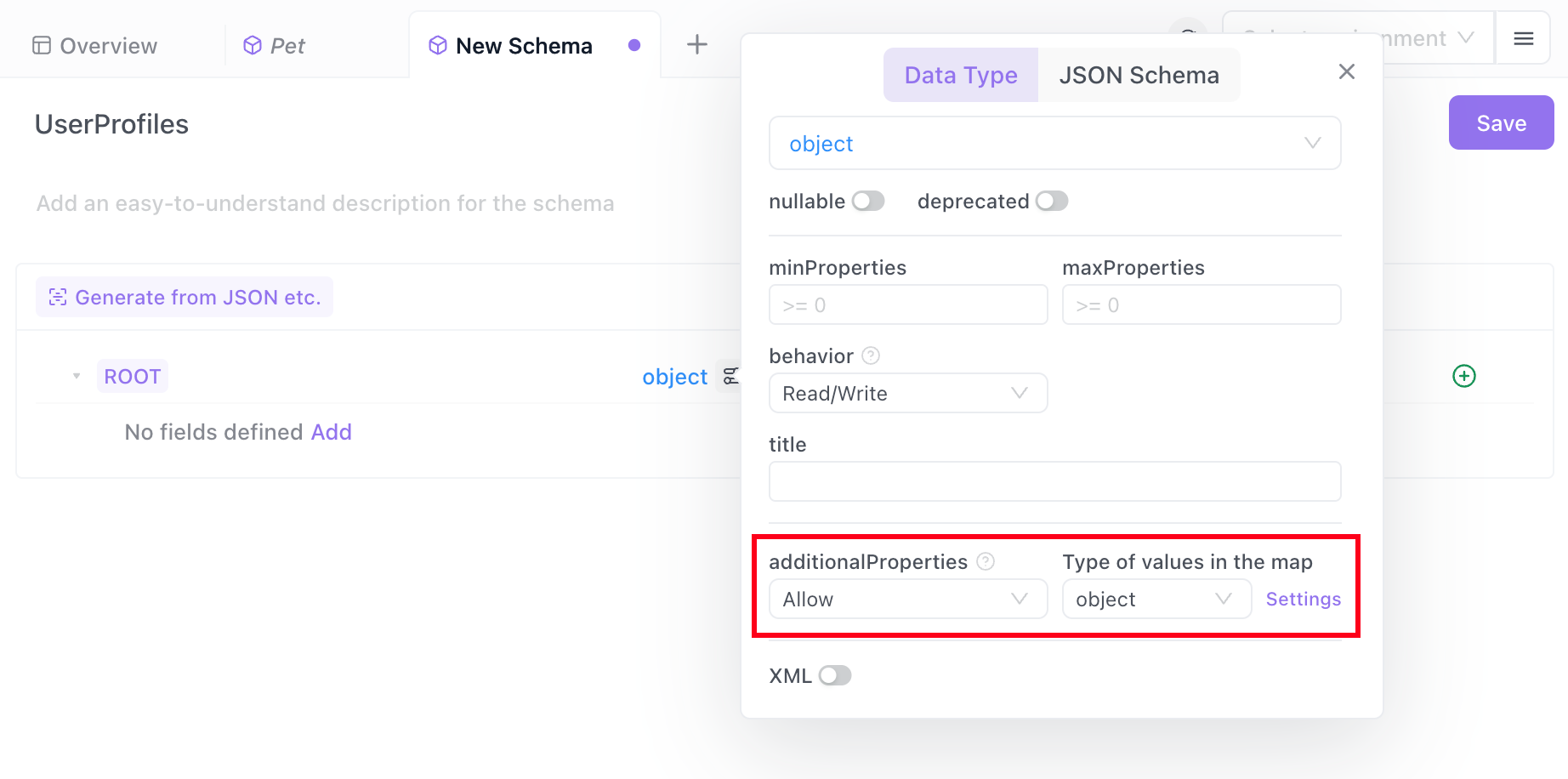

In the pop-up, add the required user information, with the user's name and email as fields of the object. It saves automatically.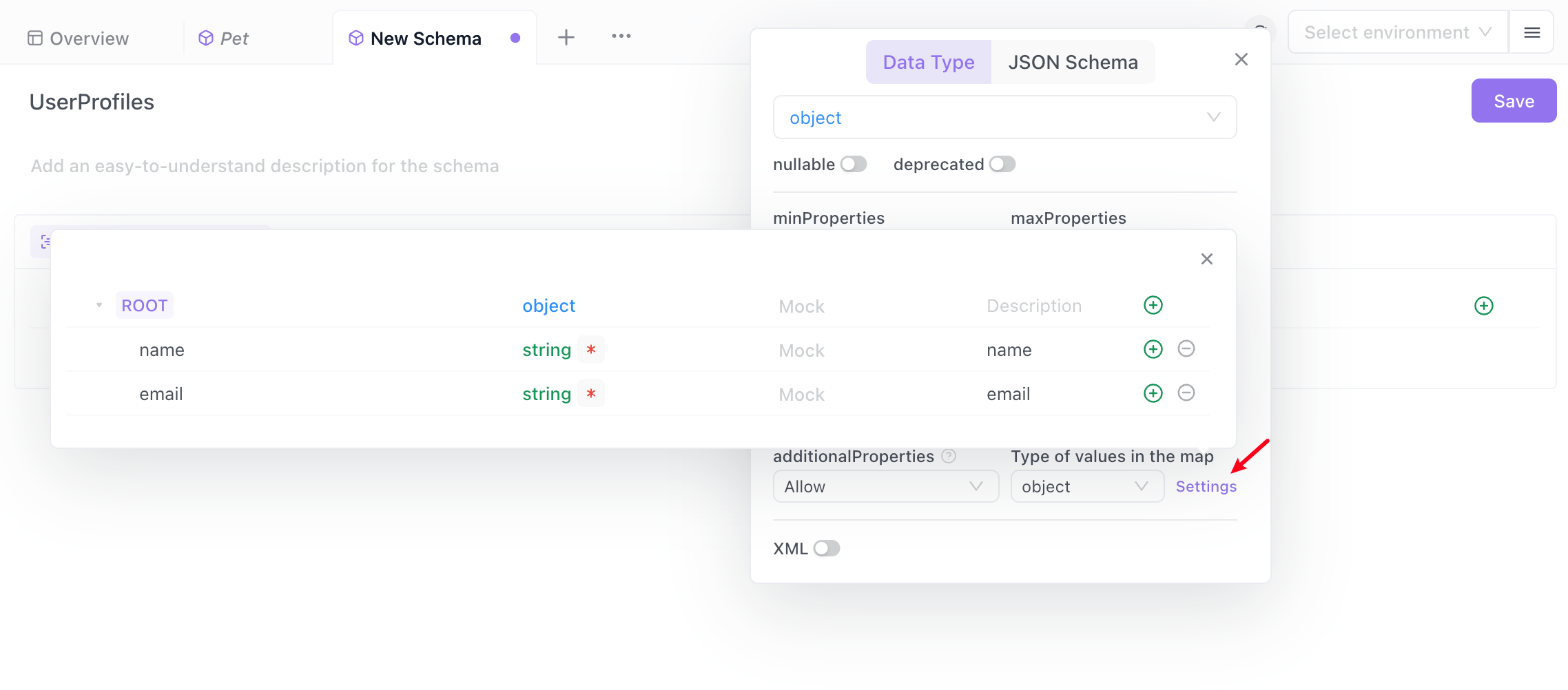

In the API documentation's responses, reference the schema at the root node and select "user profiles" that you just created.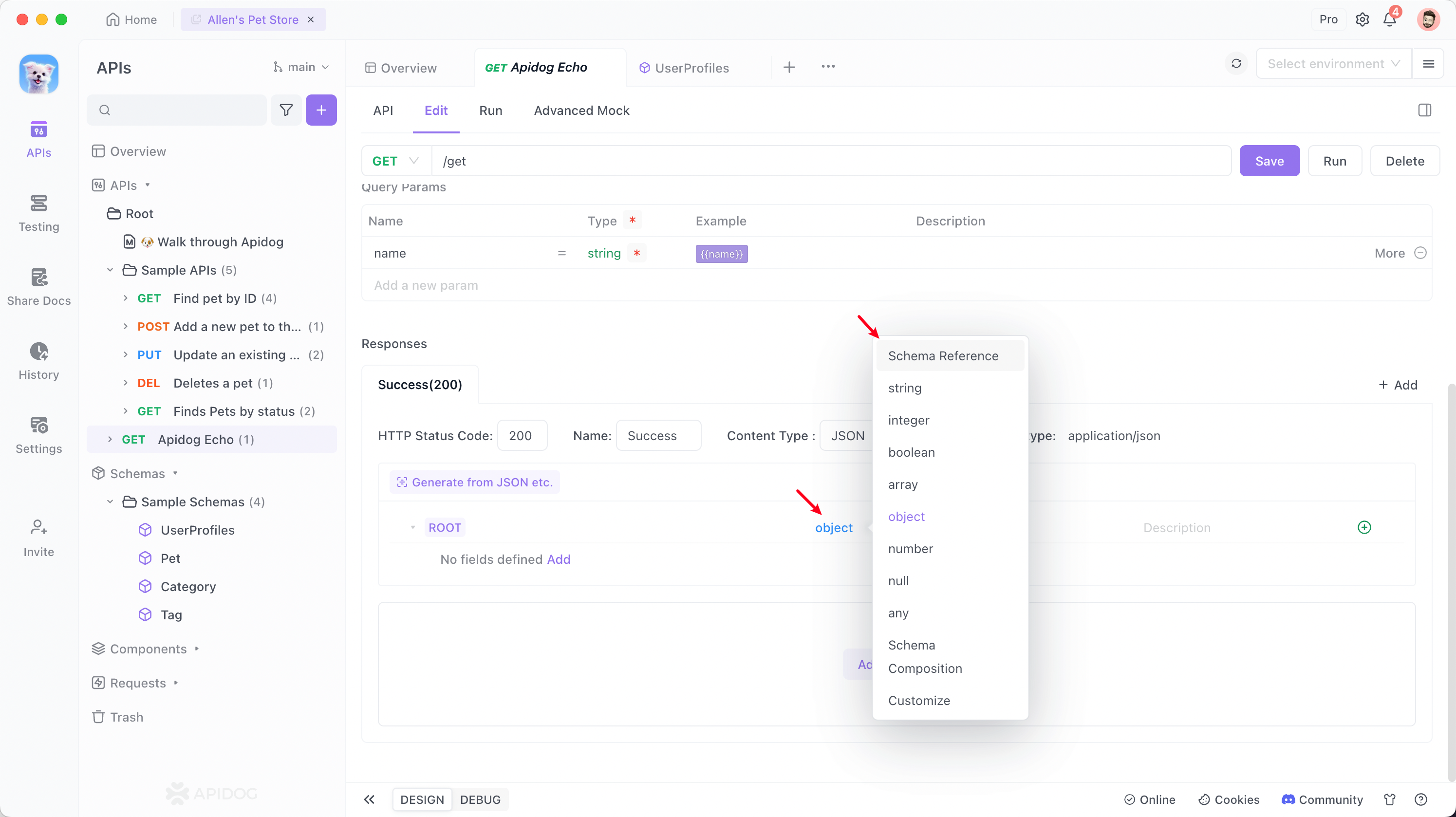

Click save, and then you can see the defined schema and example values in the return response example within the API documentation.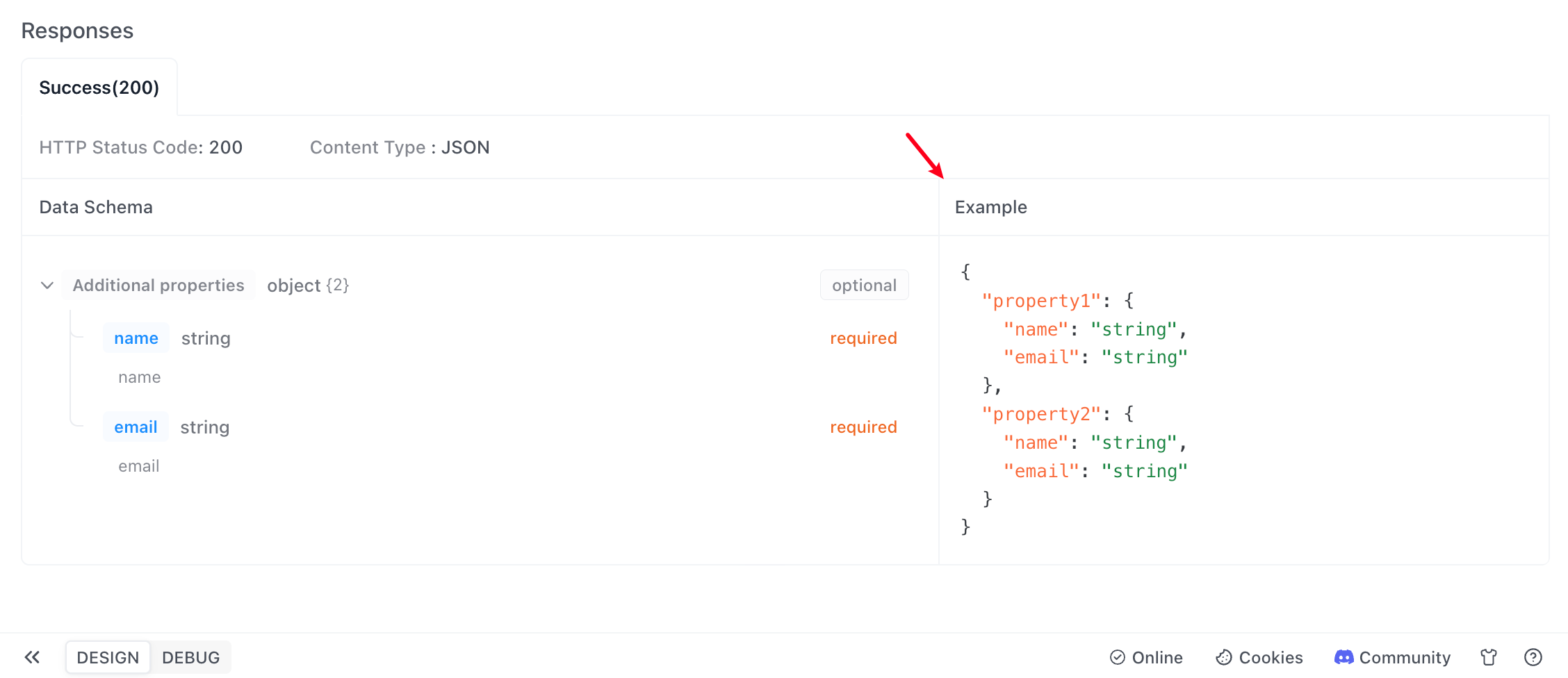

Objects with additionalProperties
name and email. Now, with the system upgrade, you want to include other fields.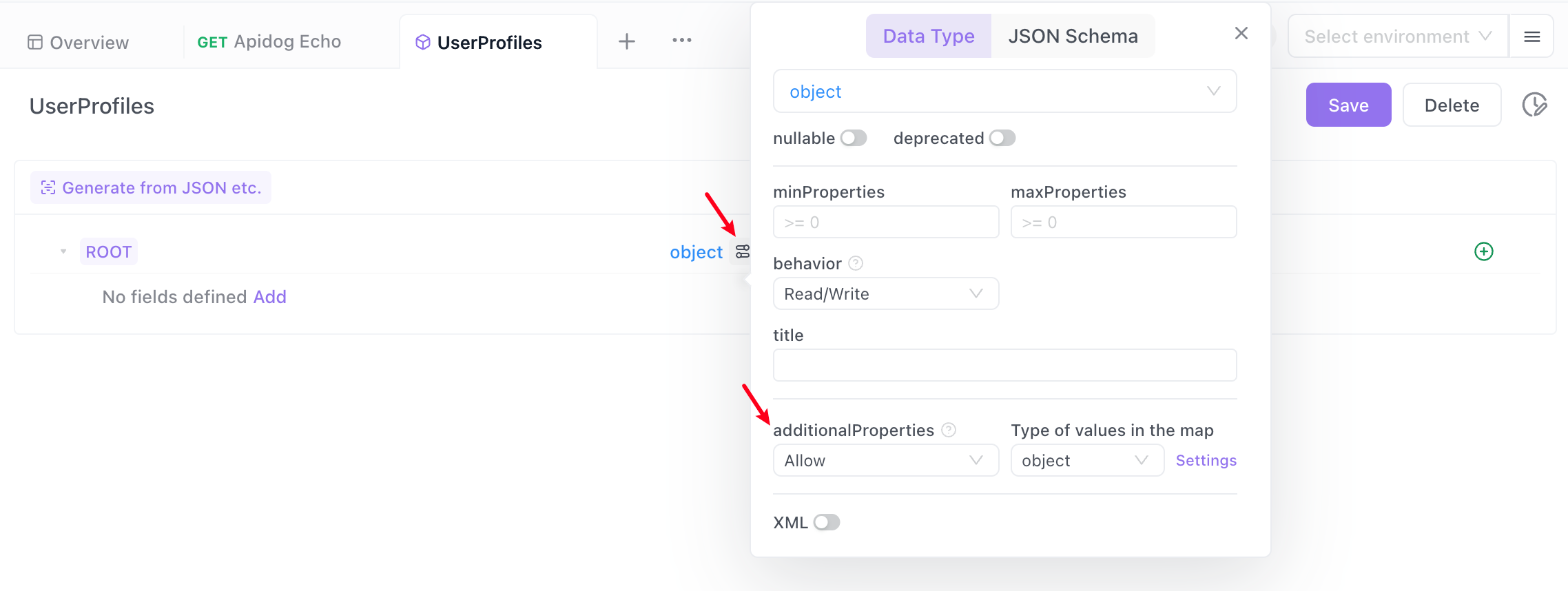
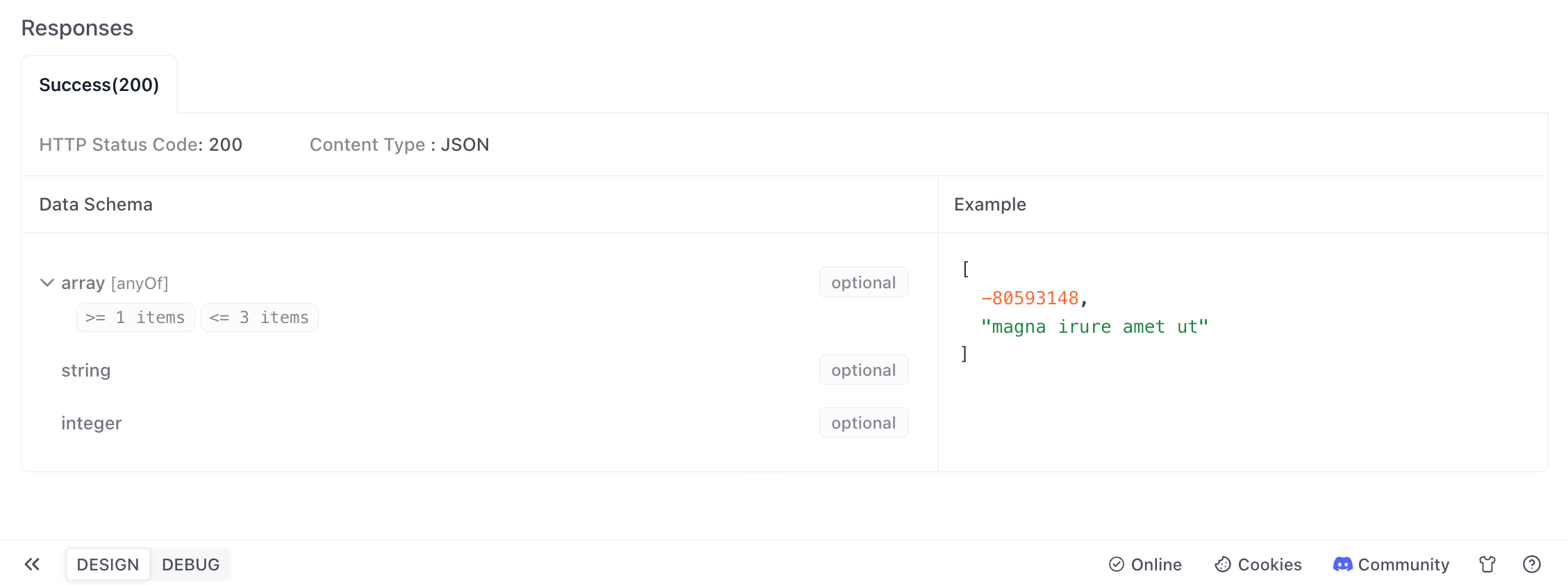
Tuples
(0,"A",2,"C"), you can set the element type to array in the data model, then set the type of items to anyOf in the combination pattern, and then add child elements of type string and integer respectively.TIP
Tools
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Generate from JSON etc. | This tool allows you to automatically generate schemas from JSON, XML data, and other sources, or directly from database table structures. Learn more about Generate schemas from JSON etc.. |
| Preview | This tool creates mock data that adheres to the schema definition, providing a preview of the expected data. |
| Generate code | This tool can produce data structure definition code in various programming languages. Learn more about Generate code. |
| JSON Schema | This tool allows direct editing of JSON schemas for fine-tuning and customization. |
FAQ
Modified at 2026-01-13 03:13:43